After a thorough analysis, a group of researchers found more than 200 vulnerabilities in nine of the most popular WiFi routers, which reside even on devices running their latest firmware versions. The routers analyzed were produced by Asus, AVM, D-Link, Edimax, Linksys, Netgear, TP-Link and Synology.
IoT Inspector researchers focused on the most commonly used devices in home environments and small businesses; Florian Lukavsky, founder of the research firm, mentions that the group contacted the manufacturers to test the latest firmware versions and thus perform a more reliable test.
According to the report, many of the routers analyzed are vulnerable to the exploitation of known flaws that should have already been addressed, as there are also publicly available exploits; the devices most exposed to attacks are the TP-Link Archer AX6000 and Synology RT-2600ac routers, with 30 vulnerabilities each.
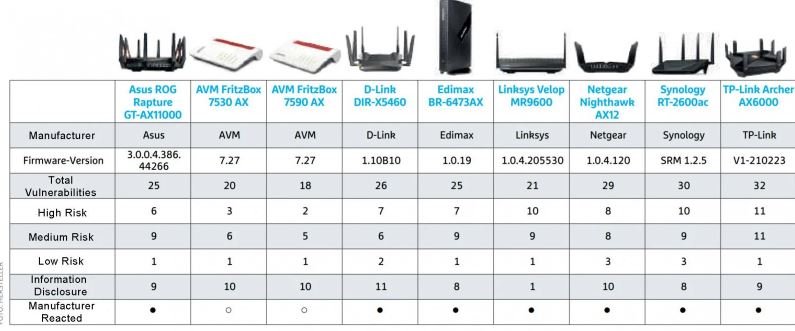
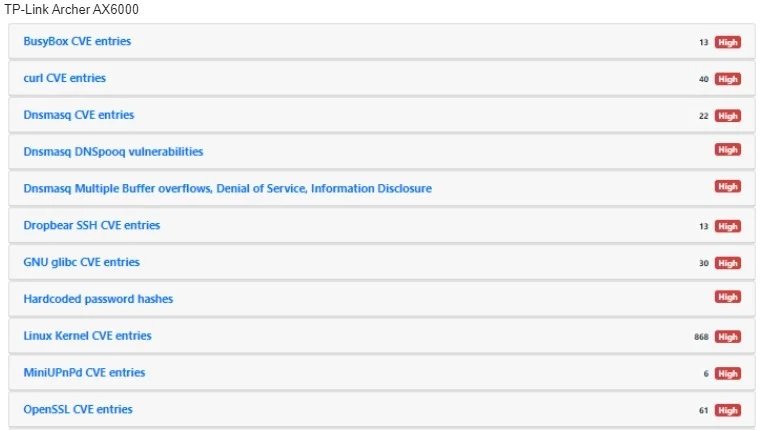
Although not all vulnerabilities are considered critical, it is possible to create some risk scenarios with the exploitation of some of these flaws. Among the most severe problems are:
- Use of obsolete Linux kernel in firmware
- Outdated media and VPN features
- Use of very weak default passwords (“admin”, “0000”, among others)
- Use of credentials encoded in plain text
For IoT Inspector, the biggest security risks are the use of easy-to-guess default passwords and the storage of passwords in plain text. For a threat actor it would be relatively simple to compromise a large number of devices with weak passwords and, in more complex cases, extract the password in plain text from a vulnerable router.
Manufacturers of vulnerable devices received the report and began releasing corresponding security patches. Vendors have already addressed most of the 266 security bugs found, though there are still some unpatched issues; the good news is that most of these vulnerabilities do not pose a major security risk to the affected devices.
Users of routers from these manufacturers are advised to apply all available updates as soon as possible, in addition to changing the default password of these devices, which will mitigate the risk of exploitation. Other security measures include disabling remote access, UPnP ports, and WPS functions if their use is not required.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
