A group of cybersecurity specialists managed to chain two vulnerabilities to take control of dashboards running MyBB online forum software, widely used by websites around the world. This report was prepared by Simon Scannel and Carl Smith, independent investigators.
The flaws were fixed after the developers received the report, so experts decided to publish more details about their finding. According to experts, the attack consists of chaining a SQL injection flaw and a cross-site scripting attack (XSS): “MyBB forums running versions between 1.8.16 and 1.8.25 are affected by these two flaws that can be chained to execute remote code on the compromised system,” the report states.
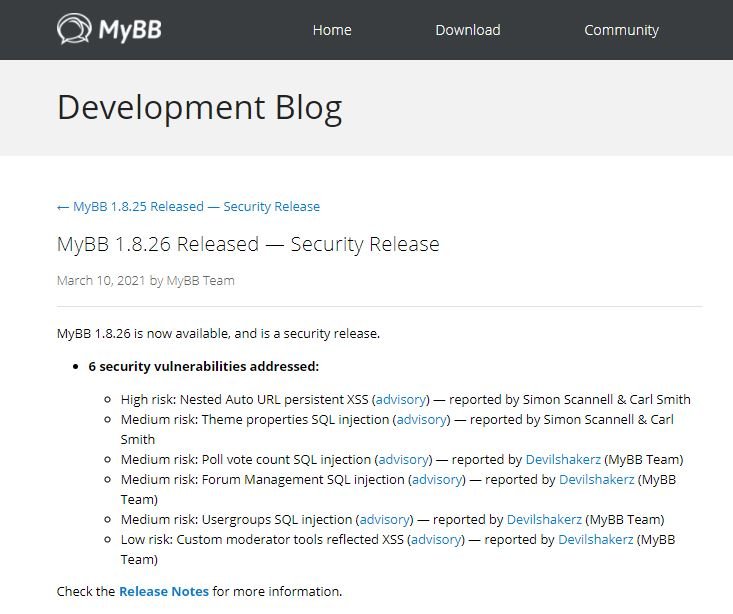
Vulnerable system compromise is possible even without previous attacks on specific MyBB installations. The first flaw, identified as CVE-2021-27889, involves serious security deficiencies in the MyBB rendering process, allowing non privileged users to insert payloads stored in posts on these forums.
On the other hand, the second flaw (CVE-2021-27890) is related to a SQL injection vulnerability to trigger remote code execution.
Researchers also discovered a mechanism to combine these flaws and trigger remote code execution. Exploiting the flaws is complicated, but possible as long as a specific MyBB administrator can be tricked into opening a booby trap message, as explained by the two researchers.
More advanced threat actors can develop an exploit to abuse the XSS flaw and then send a private message to a vulnerable administrator. If the target administrator opens this message, the exploit will be triggered. The flaws were revealed to MyBB on February 22, so a security patch was released this March 10.
MyBB is open source software written in PHP and used by around 10 thousand websites. Recently updated updates also address four minor flaws, discovered by MyBB security teams.
Finally, a representative of the MyBB development team said he appreciated the opportunity to work with security researchers before offering his opinion on the particular issues discovered by Scannell and Smith: “The corrected chain of exploitation exploits some areas of weakness related to legacy code identified a few months ago.”
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
