Trend Micro’s cybersecurity specialists have been analyzing security incidents associated with the malware variant known as SLUB for months, en allow them to make interesting findings about how it works. Although in previous incidents threat actors targeted Implementations of Slack and GitHub, the latest attack campaign focused on the Mattermost online chat service, abusing its open source to perform malicious actions.
Mattermost developers acknowledged the incident through a statement, noting that this is a violation of their Terms of Use. Mattermost also shared a method by which users can report malicious use of this platform.
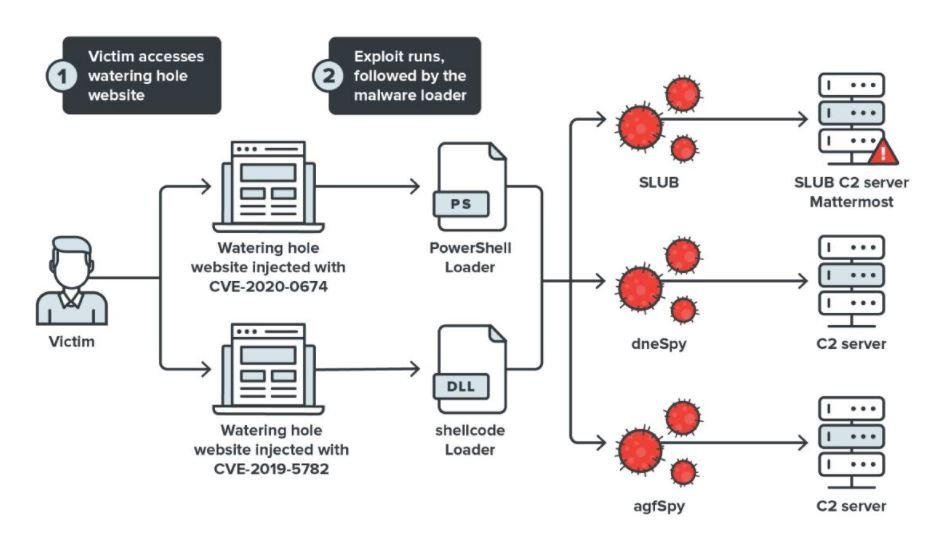
During the analysis of this campaign, called Operation Earth Kitsune, experts found five command and control (C&C) servers, seven malware samples, and four different types of errors that threat actors have used to infect websites with SLUB. According to Trend Micro, the National Korean-American Coordination Council (KANCC) has been directing users of its website to the Hanseattle platform.
“Users who accessed this site were redirected to a CVE-2019-5789 proof-of-concept (POC), a vulnerability present in Google Chrome’s chromium system,” the report states. Researchers mention that this attack not only relates to an armed version of the Chrome exploit, but also infected victims with three different malware samples.
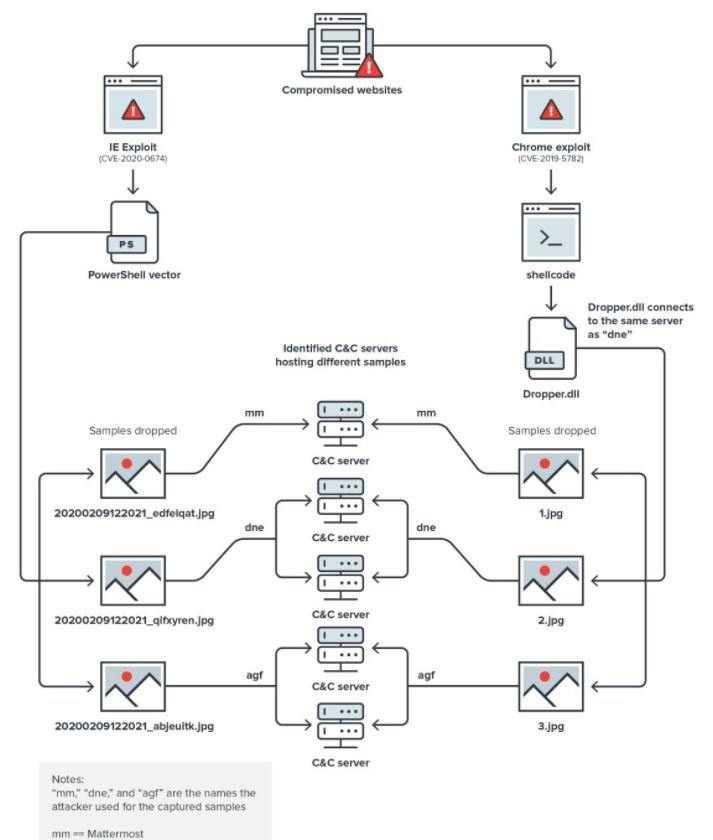
Threat actors also used CVE-2020-0674, an Internet Exploter failure that could have put thousands of websites at risk using a PowerShell loader that connected to the same C&C servers as the PowerShell used to exploit the previous failure. Finally, malicious hackers exploited flaws like CVE-2016-0189 and CVE-2019-1458. In addition to the sites mentioned during this campaign, compromised servers use GNUBoard Content Management System (CMS) versions 4 or 5.
SLUB attacks are not the only component of this campaign, as researchers detected two additional malware variants identified as dneSpy and agdSpy, whose goal seems to be to give hackers additional control over the compromised system. The investigation is still ongoing, so more details about the operators of this malicious campaign could be revealed shortly.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
