The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) announced a $150 million fine against Twitter after discovering that the company used the phone numbers and email addresses used for multi-factor authentication of its users for advertising purposes. The social platform began collecting this information in 2013 in order to protect its users’ accounts, although it avoided informing them that this data would also be used to share with advertisers.
According to the report, this practice represents a direct violation of the FTC Act and a Commission administrative order prohibiting companies from misrepresenting their security practices and using misleading terms for their benefit. The order was issued after a hacking group gained control of Twitter between January and May 2009.
The disclosure of this data would have affected up to 140 million users, so the Commission decided to resort to this millionaire fine. U.S. Attorney Stephanie M. Hinds said: “This fine reflects the seriousness of the allegations against Twitter and the new enforcement measures that will be imposed, helping to prevent further deceptive tactics that could be a privacy threat to users.”
Moreover, Twitter agreed to pay the fine and review its compliance measures to improve its data privacy practices. The company apologized to its users for the handling that was given to this information, acknowledging that “it could have been accidentally used for the publication of targeted ads.”
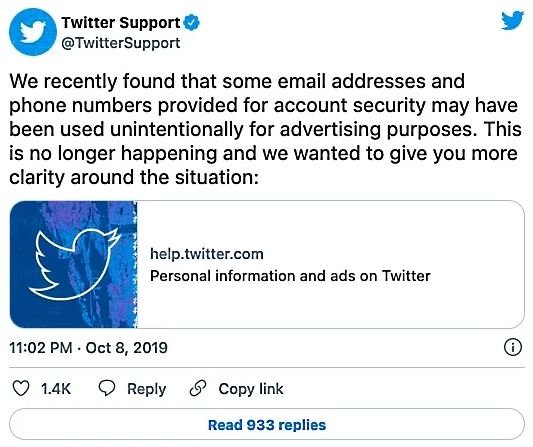
In addition to reviewing its current policies, Twitter must comply with other FTC guidelines, including:
- Notifying the Commission of any data breach incident
- Limit their employees’ access to your users’ sensitive information
- Enable new multi-factor authentication alternatives
Something similar happened in 2018 when Facebook created advertising profiles for all of its users, including records like 2FA phone numbers, account preferences, and even friend list details. Facebook even used these phone numbers as an additional vector for selling data to online advertisers.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
