The implementation of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology is one of the most important changes for public and private organizations around the world, allowing users to establish communications using a session initiation protocol (SIP) for media transmission.
Like any other Internet-connected device, VoIP devices are susceptible to exploiting security vulnerabilities. Security Affairs researchers published a report that mentions that about 38,000 devices potentially exposed to all kinds of flaws, with US firm Aastra-Mitel producing more unsafe devices.
Abuse of these compromised devices would allow threat actors to deploy denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and even some Man-in-The-Middle (MiTM) variants, which could allow for subsequent hacking variants.
Security Affairs researchers analyzed hundreds of thousands of VOIP/SIP-enabled public-facing devices, excluding honeypots, enabling the identification of vulnerable devices. Specialists also analyzed the databases available to identify the most common vulnerabilities affecting this kind of technology, making interesting findings.
Internet-identifiable devices
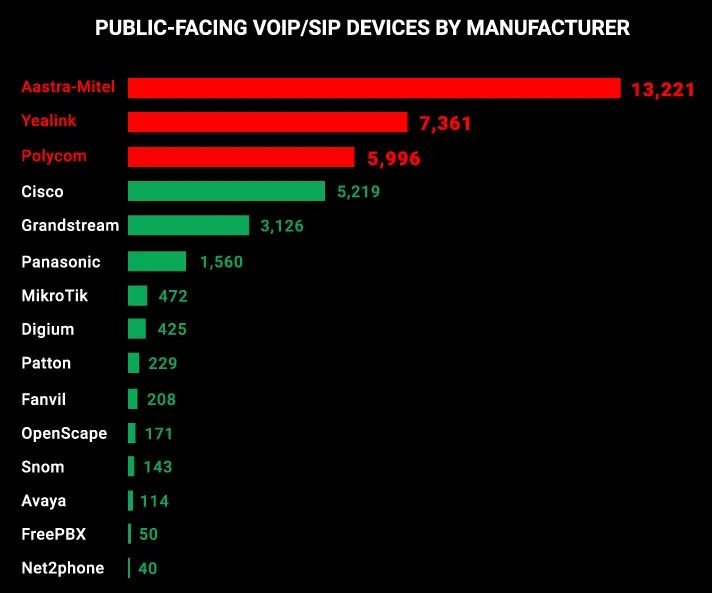
As mentioned in previous paragraphs, Aastra-Mitel is the manufacturer that produces the most easily identifiable VoIP products, with around 13,000 devices exposed. Second is the Chinese company Yealink, producing about 7,500 easily identifiable devices on the Internet. The top 3 is completed by the US firm Polycom, with about 6,000 devices.
While this does not mean that these devices pose a security risk, it does confirm that it is possible to find these devices from anywhere in the world using the IP protocol.
Security flaws
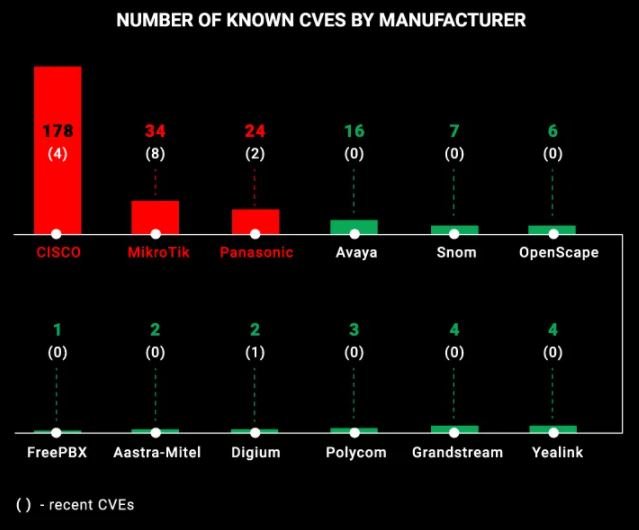
The next step was to search the MITRE CVE databases to verify which manufacturers have the most security vulnerabilities on their devices, discovering that only 5 of the 15 scanned signatures are free of security flaws (Patton, Net2phone and Fanvil).
In this area, the Cisco technology giant, whose VoIP products are affected by a total of 178 known vulnerabilities, stands out (dishonorably). It should be noted that the vast majority of flaws detected on these devices have been eventually patched. After Cisco, the Latvian-based firm Mikrotik appears. Experts point out that these devices are affected by 34 known flaws, many of them recently discovered.
Finally, Japanese firm Panasonic sees its VoIP products affected by at least 24 known CVE flaws, two classified as critical.
Location of vulnerable devices
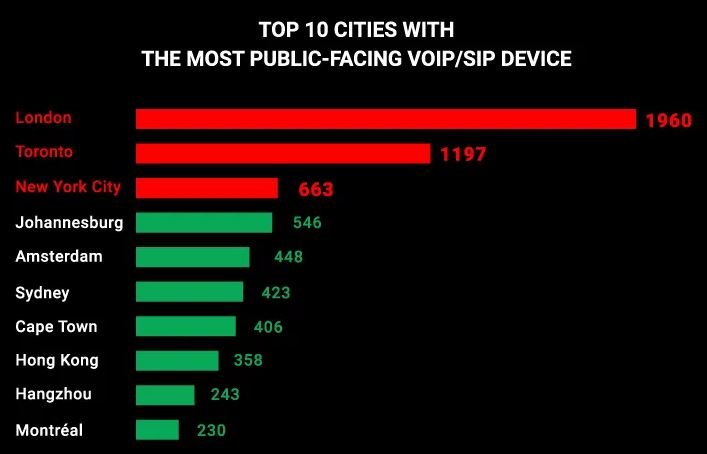
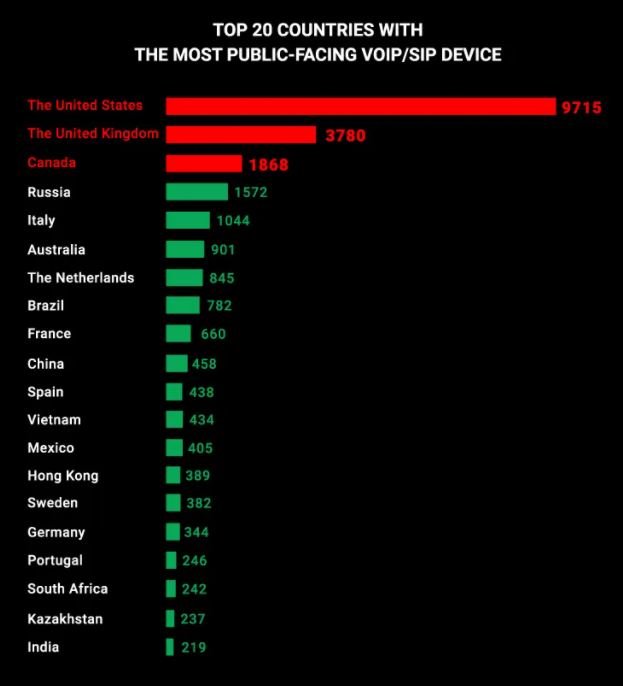
With a simple search the experts were also able to identify the exact location of the analyzed devices. Most of these products are found in the United States (9 thousand 700), followed by the United Kingdom (3 thousand 780) and Canada (2 thousand).
On cities where more vulnerable devices can be found, New York ranks first (663). Places 2 and 3 are shared by the cities of Johannesburg and Amsterdam.
Location by manufacturer
The aggregated data shows a territorial domain of some manufacturers. Nearly 7,000 Aastra-Mitel devices dominate the market in the United States and the United Kingdom.

Yealink devices also stand out in the United States, with around 1,000 computers in use.
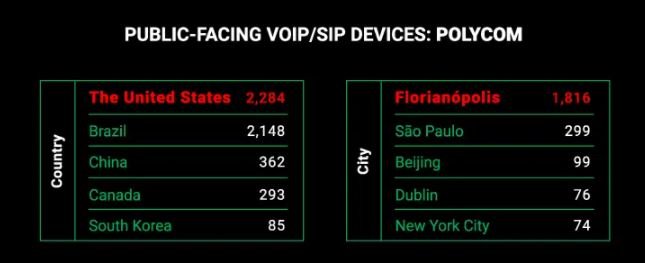
Polycom has also seized a significant market share in the U.S., as experts detected around 2,200 VoIP devices in this country.

While this analysis does not yield specific data on the number of security incidents related to VoIP technology, it is important to note all security risks potentially associated with these deployments. Manufacturers must keep their firmware updated to prevent potential data leaks or cyberattacks that can jeopardize an organization’s operations.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
