The Python Package Index (PyPI) registry removed several Python packages this week that aimed to steal users’ credit card numbers, Discord tokens, and provide code execution capabilities to threat actors. These malicious packages were posted under three different PyPI accounts and are estimated to have been downloaded more than 30,000 times.
These packages were analyzed by researchers Andrey Polkovnichenko, Omer Kaspi and Shachar Menashe, who captured the PyPi log and divided the packets into the following categories:
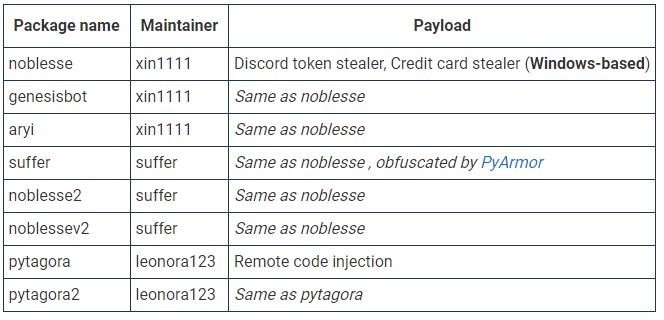
According to the analysis, most packages are capable of stealing Discord tokens, payment card numbers, and web browser-related files that could facilitate remote code execution attacks. Contrary to what you might think, all the packages identified employ very simple obfuscation techniques, probably established by novice developers.
Those responsible for this hacking campaign did not just experiment with obfuscation, but also devised new methods for the distribution of the malicious code: “This malware family is falsely advertised as optimization packages, sending potential victims messages like ‘This module optimizes your PC for Python’ across multiple platforms” , the experts mention.
The attack becomes more dangerous considering that a large number of users usually store this sensitive information in their web browsers in order to save time when performing transactions or logging into the various online platforms. A separate report also noted the removal of some npm packages designed to steal Chrome users’ credentials through abuse of legitimate password recovery tools.
On the other hand, a report by the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) notes that 66% of attacks focus on the provider’s code, in addition to an increase of up to 400% in supply chain attacks is expected by the end of 2021.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
