The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) framework, which is used by cybersecurity experts and manufacturers to convey data about software vulnerabilities, is undergoing significant revisions. CVSS 4.0 is now available for public preview, marking the first substantial upgrade to the framework in seven years. To further assist enterprises in accurately assessing and prioritizing their vulnerability management procedures and preparing defenses against cyberattacks, the numerical score may be portrayed as a qualitative severity rating (such as low, medium, high, and critical).
Additionally, the user is provided with the ability to evaluate the real-time danger and effect, providing them with important data that will assist them in defending themselves against an attack. Concerns have been raised over the widespread use of CVSS Base Scores as a method of (inadequately) evaluating risk, which led to the development of CVSS 4.0, which makes substantial efforts to enhance how risk is assessed. It also provides additional guidelines for Operational Technology (OT) and a broad variety of supplementary measures, one of which is titled “Vulnerability Response Effort” and is graded as “low, moderate, or high.”
However, the most recent update represents a huge step forward with increased capabilities that are essential for teams, with the necessity of integrating threat information and environmental measurements for correct scoring being at the center of this aspect of the game.
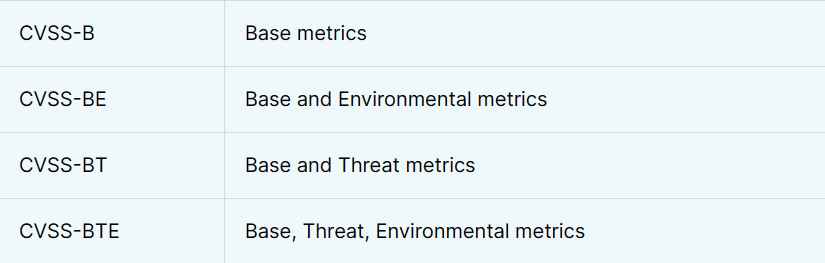
The nomenclature is also an important function to take into consideration. CVSS is not limited to merely the Base Score; thus, in order to emphasize this new nomenclature even more, it has been included in version 4.0:
CVSS-B stands for the CVSS Base Score.
CVSS-BT, which stands for CVSS Base plus Threat Score
The acronym CVSS-BE stands for CVSS Base plus Environmental Score.
The CVSS Base, Threat, and Environmental Score is abbreviated as CVSS-BTE.
As concerns about cyber security continue to quickly expand around the globe, global collaboration has never been more important in the effort to keep the internet secure for everyone. Furthermore, the development of programs such as CVSS 4.0 is necessary for both the industry and the general public.
The Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS), which is described as “a data-driven effort for estimating the likelihood that a software vulnerability will be exploited in the wild within 30 days,” and the Stakeholder-Specific Vulnerability Categorization (SSVC), which is described as a “decision-tree system for prioritizing actions during vulnerability management,” were both released before the beta version of CVSS 4.0 was made available.
Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.
