Cybersecurity experts report that a group of malicious hackers is abusing Apps Script, an enterprise application development platform maintained by Google in order to steal financial information from users, mainly credit cards.
“Hackers use the reputation of domains like script.google.com to evade anti-malware scans and rely on controls like CSP,” Sansec’s experts report. In this campaign, the legitimate domain is exploited to evade detection and security controls on attacked systems, as the domain is whitelisted by default.
The attack begins with the commitment of some e-commerce websites, on which a small piece of malicious code is injected:
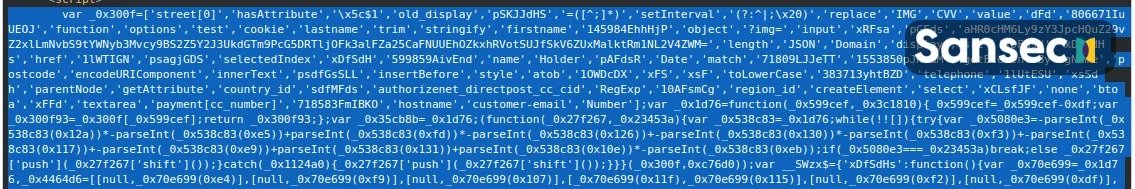
Experts mention that the malware used in this campaign was designed to intercept payment forms and send the data to a custom app, hosted in Google Apps Script.
The report also mentions that the actual code hosted on Google is not public, but the error message displayed when you arrive at the previous script is an indication that the compromised payment data is channeled by Google’s servers to an Israeli-based site called analit’.’tech.
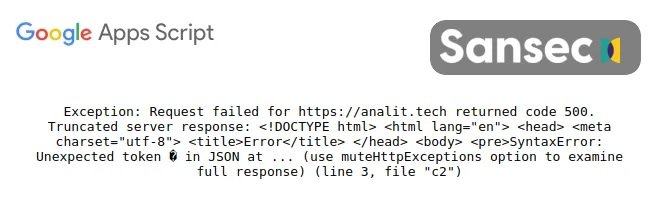
The malicious domain was registered on the same day as other domains such as hojtar’.’host or pixelm’.’tech, which have been used in other malicious campaigns for the deployment of some malware variants. Experts recommend that e-commerce site administrators ensure that attackers cannot inject unauthorized code into their platforms, as establishing proper control can prevent the highest proportion of known attacks.
On past occasions dangerous hacking groups have been detected abusing the Google Analytics service to extract sensitive information using a skimming malware. This hacking group, identified as Magecart, exploited trusted resources such as Analytics on multiple occasions to bypass content security policies using the legitimate API.
Attackers compromised the e-store using Google’s web analytics service to track visitors, so Google Analytics domains are whitelisted in their CSP settings. Cybersecurity experts have found at least twenty infected e-commerce sites around the world, including trading platforms in Europe and America dedicated to the sale of digital equipment, cosmetics, food, among other products.
To learn more about computer security risks, malware, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Cyber Security Institute (IICS) website.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
