This problem arises as the importance of cybersecurity around the globe continues to grow. The security architecture of our network is under continual attack, and it is becoming more vital that we remain one step ahead of any possible breaches. The complexity of our networks continues to increase in tandem with the expansion of our digital world. The principal gatekeeper of the network is Fortinet FortiNAC, an innovative zero-trust access solution that acts in this capacity. FortiNAC offers an unrivaled mix of visibility, control, and automatic reaction to all network connections. It has now onfronted with a new obstacle in the form of CVE-2023-33299, a major vulnerability in FortiNAC that has a high Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) score of 9.6.
Despite this, an impending danger lurks under the surface of the system. Florian Hauser, a renowned security researcher working with CODE WHITE, was the one who uncovered this issue, which is also known as CVE-2023-33299. This discovery sends a clear signal that even our most trusted networks are not beyond the reach of sophisticated security threats.
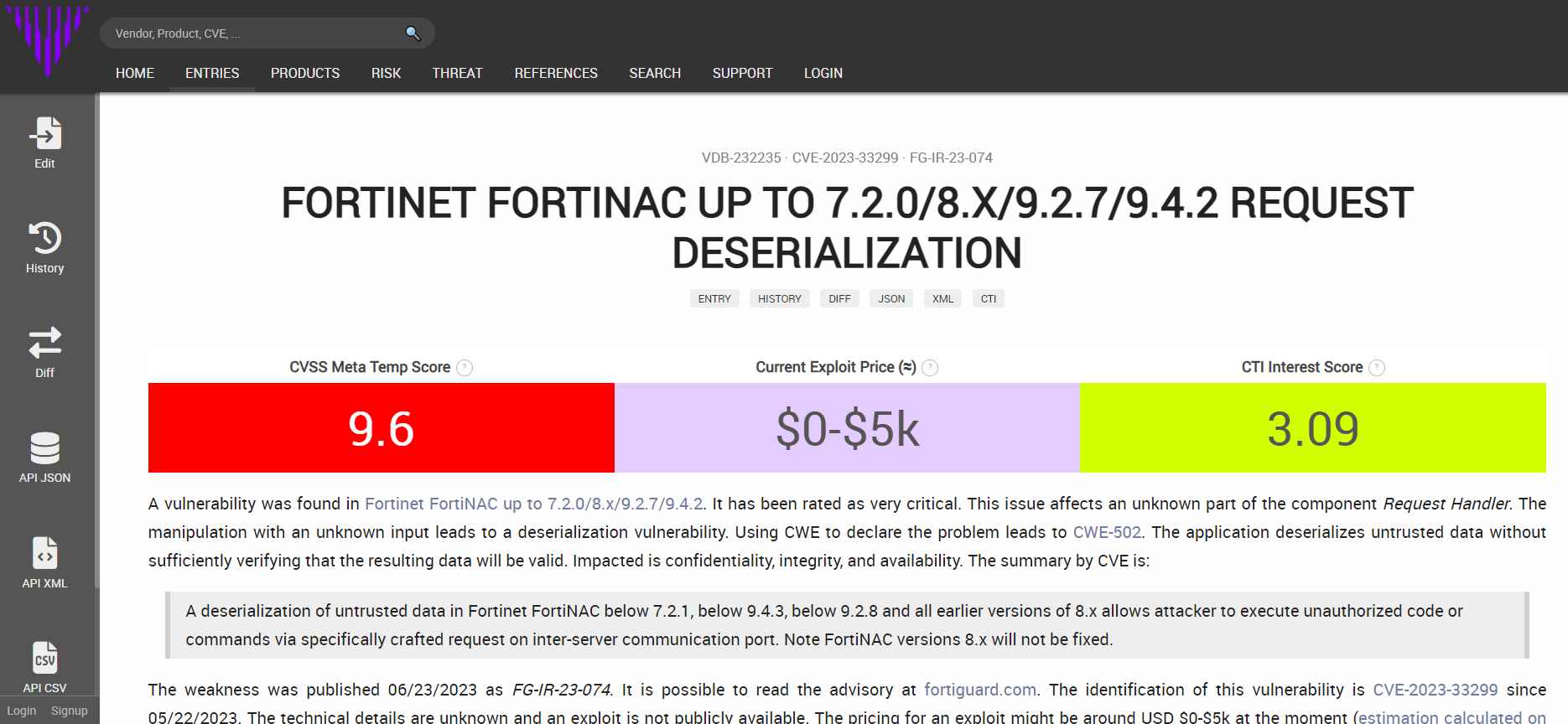
The deserialization of untrusted data vulnerability, also known as CVE-2023-33299, falls within the purview of CWE-502. Simply said, it is a security flaw that might let an unauthenticated user to execute unauthorized code or instructions by sending specially crafted requests to the tcp/1050 service.
This critical security hole offers a considerable danger since it enables malicious hackers to remotely execute instructions, which opens the door for them to possibly manipulate or steal sensitive information from systems that are impacted by the bug. This remote code execution vulnerability affects many versions of FortiNAC, including those ranging from 7.2.0 to 9.4.2. These versions have all been marked as potentially vulnerable.
Fortinet took rapid action as a reaction to this severe security issue, therefore proving the depth of its commitment to maintaining the safety and integrity of networks. FortiNAC versions 7.2.2, 9.1.10, 9.2.8, and 9.4.3 all received critical upgrades from Fortinet , which successfully addressed the issue.
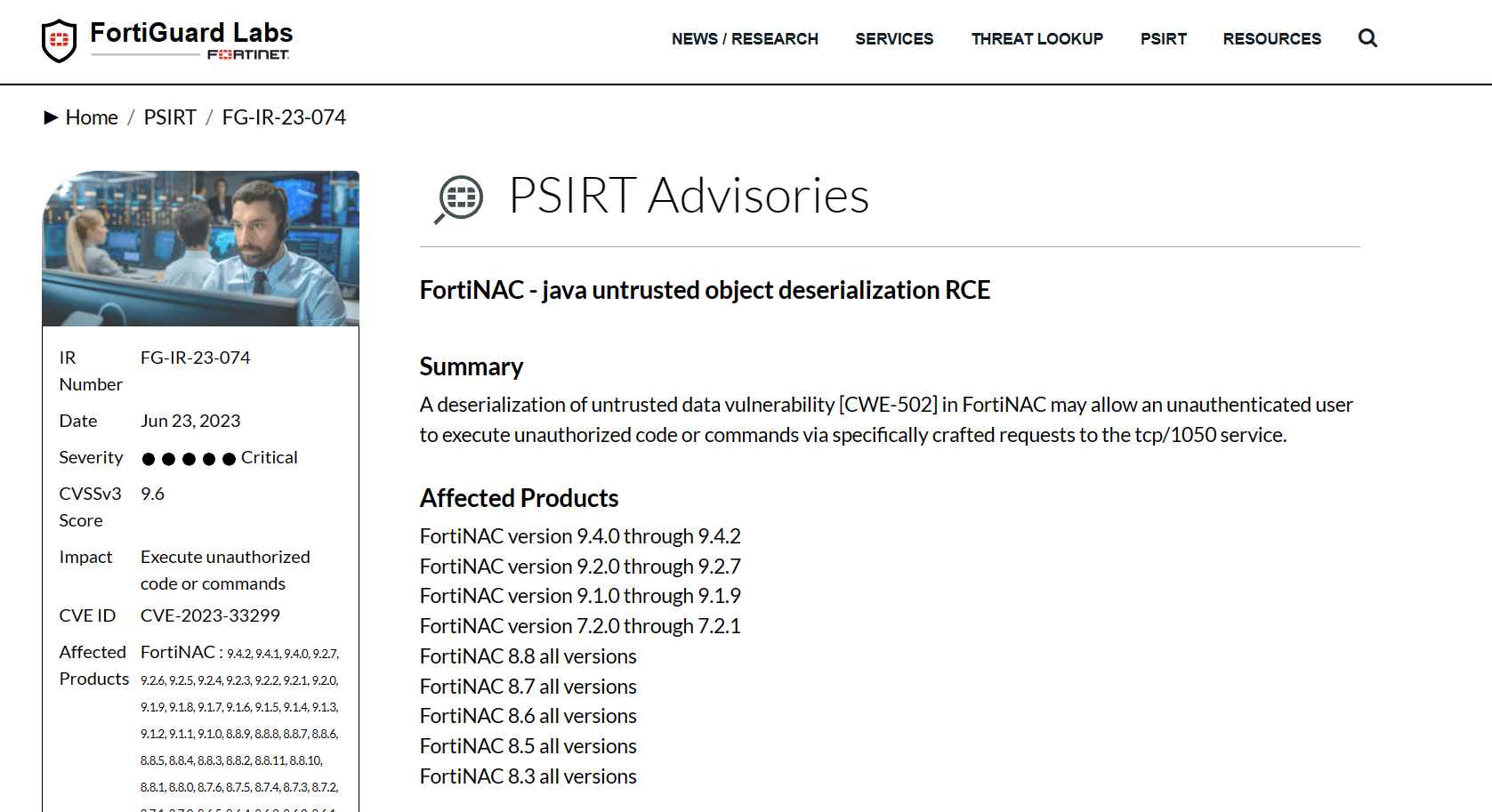
Users who are affected by CVE-2023-33299 are strongly encouraged to quickly upgrade their systems to the most recent secure versions in order to mitigate any possible risks that may be connected with the vulnerability. Even if your network hasn’t shown any evidence of an incursion, it is still a good idea to take preventative measures and strengthen your systems so that they can withstand any possible attacks.
Information security specialist, currently working as risk infrastructure specialist & investigator.
15 years of experience in risk and control process, security audit support, business continuity design and support, workgroup management and information security standards.
