Eight apps have been discovered on Google Play that were spreading new malware called Autolycos. Maxime Ingrao, a researcher at the cybersecurity firm Evina discovered the android malware or fleeceware, which he named Autolycos. This type of malware is characterized by subscribing users to premium services without their knowledge or consent and accessing SMS messages, so that the user is not aware of the charges generated until the next telephone bill arrives.
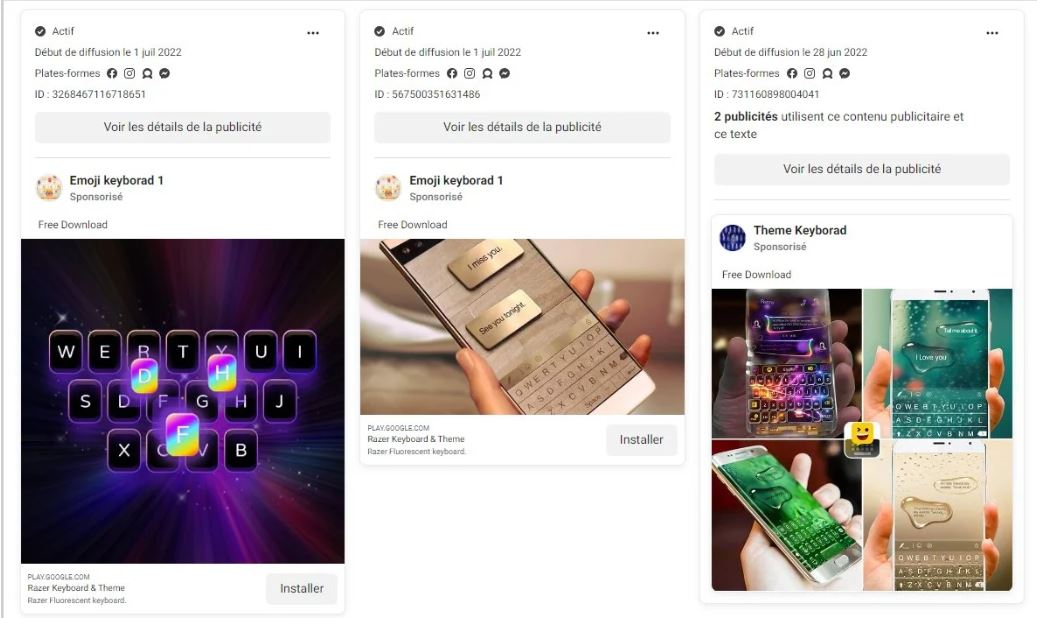
In order to spread the malicious mobile apps, the researcher discovered that the cybercriminals had created advertising campaigns in Facebook and Instagram, among other social networks. For example, for one of the malicious apps (Razer Keyboard & Theme) 74 advertising campaigns have been discovered.
After a detailed analysis of the new malware, Malwarebytes researchers have determined that it could be a new variant of Joker (Android/Trojan.Spy.Joker), a spyware discovered in 2019 that also secretly subscribed people to premium and stole messages. SMS, among other fraudulent activities.
Autolycos’ behavior allows it to evade detection more skillfully than the original Joker. Joker uses webviews to display information (such as a splash screen, installed application logo, etc.) to mislead the user while malicious processes are running in the background. For its part, Autolycos retrieves a JSON file from a C2 server and URL visits in a remote browser, returning the result to be included in future requests. This makes it less noticeable and increases the complexity of detecting that a device is compromised.
The eight Android apps that Autolycos distributed are as follows:
- Vlog Star Video Editor (1 million downloads)
- Creative 3D Launcher (1 million downloads)
- Funny Camera by KellyTech (500,000 downloads)
- Wow Beauty Camera (100,000 downloads)
- Gif Emoji Keyboard (100,000 downloads)
- Razer Keyboard & Theme by rxcheldiolola (50,000 downloads)
- Freeglow Camera 1.0.0 (5,000 downloads)
- Coco Camera v1.1 (1,000 downloads)
It should be noted that among all the malicious applications that distributed the new malware, they add up to more than 3 million downloads.
In July 2021, Maxime Ingrao discovered the malicious apps and privately reported them to Google. However, it took six months for the company to remove six of these applications from its market. Finally, Google eliminated the remaining two on July 13, once Ingrao made his investigations public.
The researcher details that it is necessary to monitor both the Internet data that is consumed in the background and the battery consumption, have Play Protect activated and minimize the number of apps installed to try to avoid this type of threat.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
