A few months ago, specialists from the security firm ThreatFabric reported the detection of a new malware variant for Android devices. Identified as Coper, this malware family appeared to be a development derived from the Exobot variant and aims at banking fraud activities. According to experts, there is a direct connection between this new variant and ExobotCompact, a lightweight version of the malware developed a couple of years after the original version. The most recent version of this new malware was released in November 2021 and has been identified as ExobotCompact.D.
The main distribution method of this malware variant is through malicious apps available on the Google Play Store. These apps were downloaded by more than 50,000 users and focused on financial services, attractive mainly to Android users in Europe. This variant not only focuses on banking fraud, since at the beginning of 2022 a series of publications on dark web forums confirmed that there is a connection between this malware variant and Octo, a banking Trojan/botnet for Android created from a malware variant of ExobotCompact.
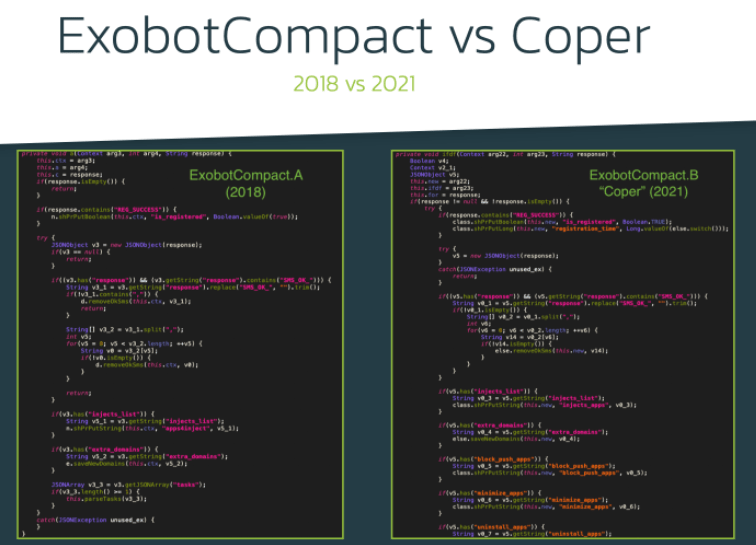
The constant evolution of the malware added advanced features, including remote access to the affected devices. Features like this allow threat actors to perform fraudulent activities virtually inadvertently, creating a major challenge for antivirus engines and researchers.
To gain remote access and control of the affected device, hackers require knowing what is going on the user’s screen and a mechanism for deploying remote actions. ExobotCompact.D is based on the built-in services that are part of the Android operating system: MediaProjection for screen streaming and AccessibilityService for performing actions remotely.
Screen streaming with MediaProjection is based on sending screenshots at a high speed, giving the operator a near real-time representation of what happens on the compromised device. When ExobotCompact.D receives the “start_vnc” command, it parses the submitted configuration along with the commands described below:
- STREAM_SCREEN: Enable screen streaming with MediaProjection
- BLACK: Enables the overlay of a black screen to hide remote actions on the device
- SILENT: Disable all notifications and lower screen brightness to a minimum
ExobotCompact.D may also collect information available on the screen, including application distribution and wallpaper. This would allow threat actors to recreate the design of the affected screen and perform even more intrusive hacking tasks. Using this information and the “vnc_tasks” command, hackers could perform various actions:
- click_at: To click on the specified coordinates on the screen
- gesture: Make gestures on the screen
- set_text: Set the specified text to the specified item
- long_click: Make long click
- action: Perform a specified action
- set_clip: Set text on clipboard
- paste: Paste data from clipboard
- send_pattern: Perform a gesture based on a specified pattern
- scroll: Scroll up/down
Although researchers have managed to determine many traits of this campaign and the associated malware, it was still unclear what Octo was. The first hints appeared in January 2022, when a user on a dark web forum pointed to the hacker “Architect” as the developer of this project. About this hacker, it is said that he uses sophisticated tools and attacks, in addition to the fact that in a Telegram channel it was confirmed that the hacker also uses the nickname “goodluck”.


In this forum it is also mentioned that the hacker has developed a private Trojan, written entirely from scratch.

When trying to find information about the hacker that Octo developed, the researchers found some similarities between ExobotCompact and the Trojan, highlighting:
- Source code protected against exo reverse engineering techniques Patented payload obfuscation
- Distribution through the Play Store
- Disabling Google Play Protect
By now, Threatfabric was clear that Octo and ExobotCompact were closely related. To test their hypothesis, the researchers examined the commands supported by ExobotCompact, comparing them to the Octo admin panel, which made it possible to identify more matches:
- Both variants have remote access capabilities and are referred to as “VNC” in both cases
- Octo panel has six time-based settings that set up delays before executing any action. This list matches exactly the same delays that ExobotCompact can receive from its C&C server
- Some of the settings, such as “minimize_delay” or “get_device_admin_delay” are typical of only these two malware variants
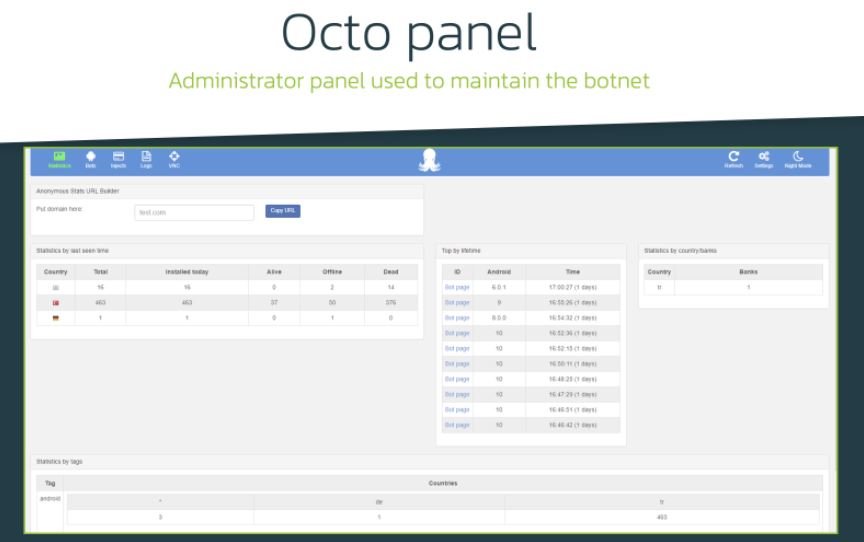
It is highly likely that ExobotCompact.D has been rebranded as Octo to add more attack variants to its arsenal and all this time has been controlled by the same hacker or hacker group. Malicious applications have already been removed from Google’s official repository, but considering the capabilities of its developers this threat should not be considered as overcome.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
