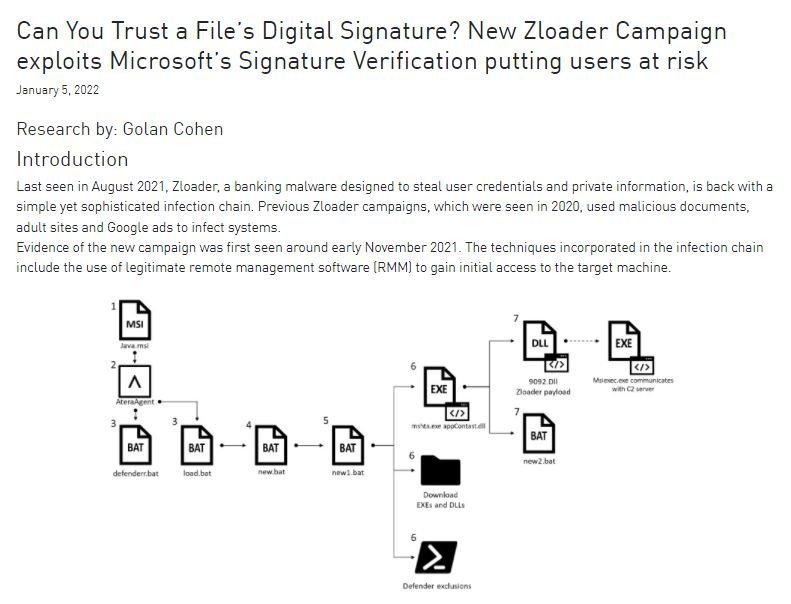
A report by Check Point Research points to the detection of a new campaign related to the ZLoader ransomware, started in November 2021 and that by now has already managed to steal the credentials of more than 2000 users. As some may recall, Zloader is a banking malware active since 2016, apparently based on the Zeus banking Trojan.
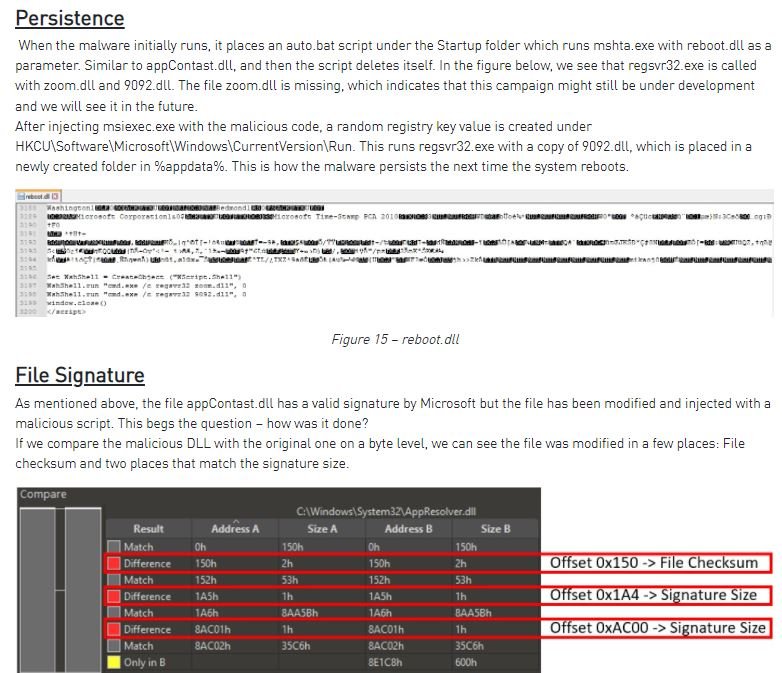
Experts mention that the attack leverages remote management software implementations to access the affected device without raising suspicion. According to the report, the infection begins with the compromise of the Atera software, which would eventually allow monitoring and administration of the affected system, eventually leading to the ransomware infection. In the final stage of the attack, the malware exploits Microsoft’s digital signature verification method to inject its payload into a signed system DLL in an attempt to evade detection.
In its report of the attack, Microsoft mentions that the remote code execution vulnerability resides in the WinVerifyTrust function, as it handles the verification of Windows Authenticode signatures for portable executables. Threat actors could trigger an attack by modifying a signed executable file to exploit unverified parts of the file, adding the malicious code to the file without validating the signature.
Experts also found an open directory, hosted on teamworks455.com and containing some of the files being downloaded as part of the attack. Malware operators also change files every few days; the analysis of the ‘entries’ of the file allowed recovering the list of victims who are infected with Zloader and their country of origin.
This campaign was attributed to MalSmoke, a well-known hacking group responsible for other prominent cybersecurity incidents. Experts came to this conclusion by analyzing the tactics employed by hackers, mainly the use of legitimate software as an initial access point to the compromised system.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
