A group of experts created an experiment to show that, using a machine learning algorithm, it was possible to guess the 4-digit payment card PIN of a payment card with an effectiveness of up to 40%, regardless of whether users covered the keyboard of an ATM machine with their hand.
For these tests, the researchers employed an ATM replica that allowed the machine learning algorithm to perform better analysis based on indicators such as machine dimensions and key space. Once the required hardware was set up, the machine learning model was trained to recognize the keystrokes of each key and determine possible combinations, also relying on videos of dozens of people using ATMs.
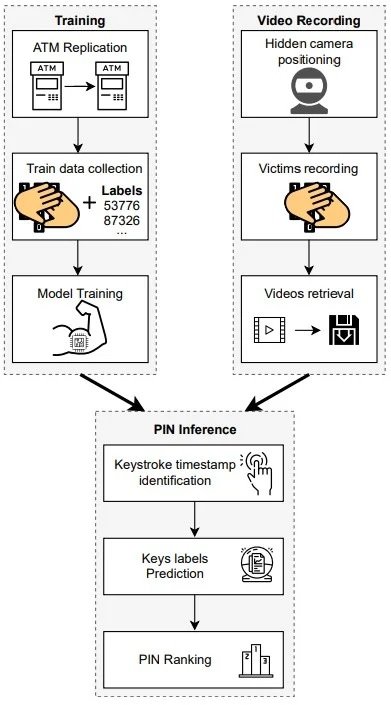
For algorithm training, the researchers used nearly 6,000 ATM video samples, in addition to 50 volunteers who entered 4- and 5-digit PIN keys into the test ATM.
The experts also employed a Xeon E5-2670 machine with 128GB of RAM and three Tesla K20m with 5GB of RAM each, which are not common implementations but are considered practical. By spending the 3 attempts that most ATMs give for correct PIN entry, experts were able to find the right key for 5-digit PINs 30% of the time, reaching 41% on PINs of only 4 digits.

The researchers mention that this model was able to exclude keys in a sequence based solely on the space covered by a user’s hand, discarding with great precision the keys that the user could not press with his hand in a certain position.
Another key in this experiment was the location of the cameras around this ATM, placed on top of the ATM. In addition, if the camera is also capable of capturing audio, the model could also use sound feedback by pressing that is slightly different for each digit, which increases the effectiveness of the analysis.
While this is a complex attack, experts do not rule out the possibility that a group of hackers could implement a similar technique in real scenarios, so the researchers recommend not dismissing the possibility of a similar attack.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
