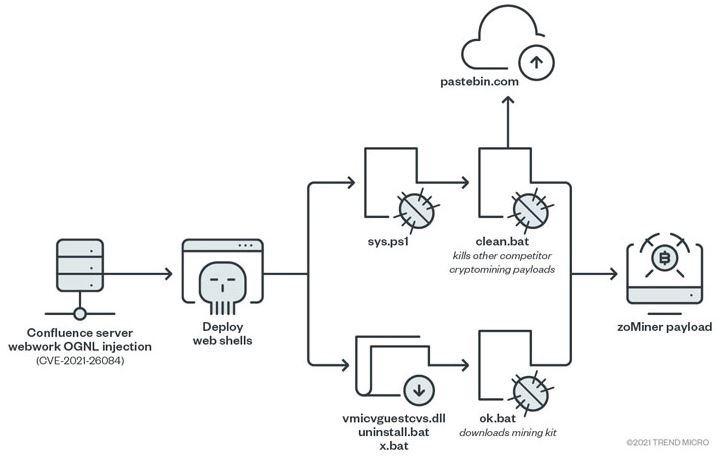
Cybersecurity specialists reported that a group of threat actors is actively exploiting a critical vulnerability in Atlassian Confluence deployments on vulnerable Windows and Linux. These attacks aim to install webshells working as crypto miners on affected systems.
Tracked as CVE-2021-26084, it was described as an Object-Graph Navigation Language (OGNL) injection flaw that could be exploited to run arbitrary code execution on Confluence Server or Data Center affected implementations. The flaw got a 9.8/10 score according to the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
The problem resides in Atlassian Confluence Server and Data Center Webwork module and exists due to the improper validation of user inputs, causing the parser to evaluate fraudulent commands injected within OGNL expressions.
Regarding the detection of this malicious campaign, experts point out that the attacks started after the US Cyber Command warned of massive exploitation attempts potentially related to the public disclosure of this flaw in last August.
Operators of this campaign use multiple malware variants, including z0Miner, a Trojan with cryptojacking capabilities detected in several incidents. Security firms like Imperva and Trend Micro agree in their thoughts about the operation mode of the attackers and the malware variants they use.
Imperva, Juniper, and Lacework also detected exploitative activity by Muhstik, a China-linked botnet known for its worm-like self-propagating ability to infect Linux servers and IoT devices since at least 2018.
In addition, the threat intelligence team Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 said it identified and prevented attacks that were orchestrated to steal passwords, as well as download malware-laden scripts that downloaded a miner, and even opened an interactive reverse shell on the affected machine.
To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
