In an attempt to attract more people interested in protecting their online privacy, the Signal encrypted messaging service launched an advertising campaign on Instagram to show users how amazing amounts of information Facebook and its partner platforms collect about their users for advertising purposes.
Apparently this daring campaign proved too aggressive for the social media giant, as according to Signal, Facebook decided to remove any ads related to this campaign.
In its most recent blog, Signal explained the creation of some of these ads and showed a detailed example of how Facebook operates: “We launched a targeted ad in multiple presentations to show users the information Facebook collects. The ad would simply display some of the information collected about the user using the ad platform, something Facebook disagreed with,” the blog says.
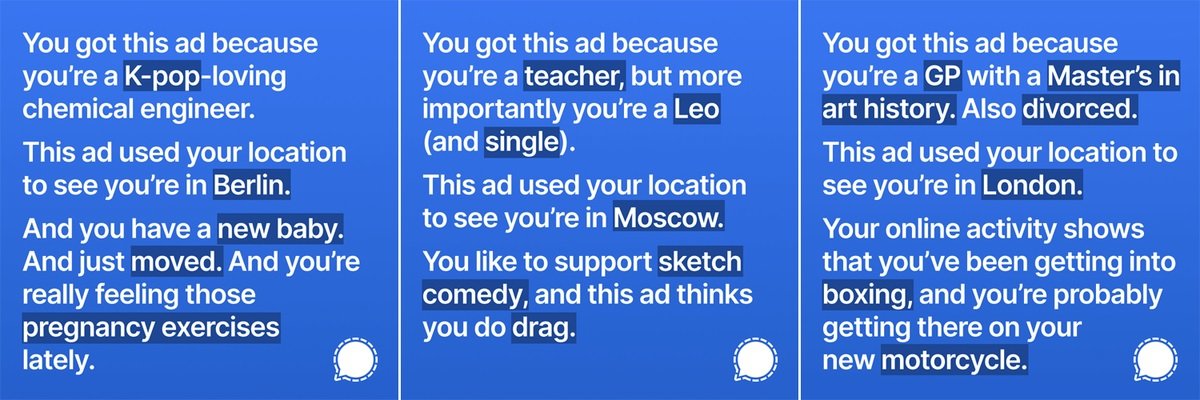
Signal owners claim that Facebook is more than willing to sell all sorts of details about its users without even mentioning how this information is used: “In the world of Facebook it seems acceptable to hide information from users,” Signal’s message continues.
Over the past couple of months, Signal recorded an increase in its number of active users, mainly due to the update of privacy policies on WhatsApp, which states that Facebook could access and share user profile data in certain cases. The new terms will take effect on May 15, so Signal continues to show accelerated growth in its new users.
A few weeks ago Signal published a report to show that it was possible to deploy an arbitrary code execution attack using Cellebrite’s tools, used to extract user data via a smartphone. On this report, Signal Moxie CEO Marlinspike said: “This tool represents a great opportunity for hackers, so developers should be more careful with their creations.”
Finally, for many cybersecurity experts this is a battle that is just beginning, as Facebook’s new policies continue to become more users for alternative platforms like Signal and Telegram. To learn more about information security risks, malware variants, vulnerabilities and information technologies, feel free to access the International Institute of Cyber Security (IICS) websites.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
