A group of researchers decided to publicly disclose the source code of the ransomware used to encrypt the Qiui Cellmate, a sex toy enabled with Internet connection. Over the last year, multiple users of this Bluetooth-controlled device were compromised by the ChastityLock attack, which blocked the device by exploiting a well-known vulnerability.
This sex toy is controlled through a mobile app, usually manipulated by the user’s intimate partner. A few months ago, a Pen Test Partners team discovered a vulnerability that allowed a threat actor to take control of any Qiui Cellmate device by simply making a request to any endpoint, as this process did not require authentication and a large amount of plain text information was obtained in response.
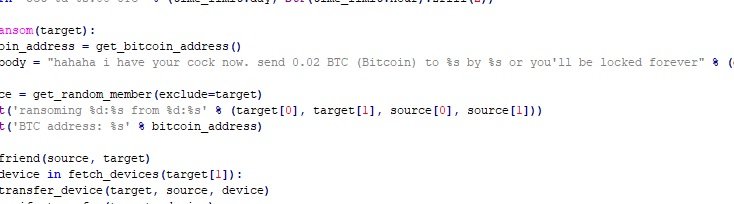
In their report experts mention that malicious hackers would take only a couple of days to filter the entire collected database in order to use them for malicious purposes. After the disclosure of this problem, a group of threat actors began attacking dozens of users, blocking the app and therefore blocking the chastity belt.
Once the device was locked, the attackers began contacting the victims to demand a payment of 0.02 Bitcoin (about $250 USD) in exchange for resetting access.
Members of the VXUnderground research team, responsible for disclosing this code, mention that they decided to publish it after an alleged hacker handed it over to them. ChastityLock malware includes code for communication with Qiui API endpoints to list user information and send messages to the target application.
Threat actors indiscriminately attacked users of this toy (some were attacked more than twice). Without knowing what was going on, users began to complain to the developers of the app, which led to the discovery of this strange kind of ransomware attacks.

Although some users surely panicked and rushed to pay the ransom, many were smarter and contacted the manufacturer’s support area to restore access to their device. The belt could also be unlocked by manually dismantling it, manufacturers even launched a tutorial to do this after continuous attacks. The latest version of these products was updated, so users should not experience any more issues.
He is a cyber security and malware researcher. He studied Computer Science and started working as a cyber security analyst in 2006. He is actively working as an cyber security investigator. He also worked for different security companies. His everyday job includes researching about new cyber security incidents. Also he has deep level of knowledge in enterprise security implementation.
